Overview
HEV drivetrain types
Not all hybrid vehicles are the same. Some use a series drivetrain and others use a parallel drivetrain.
- Series drivetrain hybrid,
- The electric motor is the only means of providing power to the wheels.
- The motor receives electric power from either the battery pack or from a generator run by a gasoline engine.
- Parallel hybrid drivetrains,
- The engine and electric motor work in tandem to generate the power that drives the wheels.
- Parallel hybrids use a smaller battery pack than series drivetrains, using regenerative braking to keep it recharged.
- When power demands are low and the battery needs recharging, parallel hybrids run the engine and use the traction motor as a generator for the main source of battery recharging.

HEV Nomenclature
Nissan uses Clutch 1 and Clutch 2 nomenclature on all of their hybrids, no matter if the transmission is transverse or longitudinal mounted.
- Clutch 1 is on the input and
- Clutch 2 is on the output
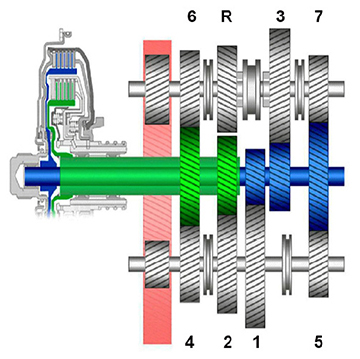
Even though the terms are very similar between Dual Clutch Transmissions (DCT) and hybrid vehicles intelligent dual clutch systems, Hybrid intelligent dual clutches are much different than dual clutches in DCT vehicles. For example, the QX30 uses a DCT transmission that shifts automatically.
The QX30 dual clutch uses one clutch to engage the odd forward gears 1, 3, 5, and 7, and the second clutch (inner multidisc clutch) to engage the even forward gears 2, 4, 6 and the Reverse gear.
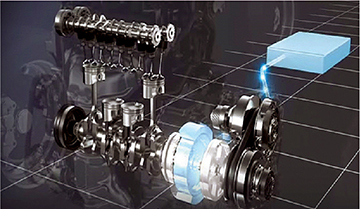
Hybrid dual clutch systems engage or disconnect the traction motor and the gasoline engine.
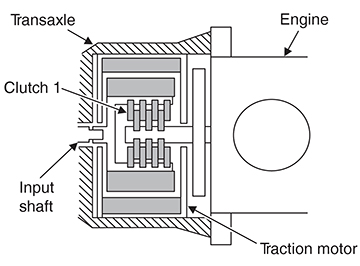
- Clutch 1 is installed in the traction motor.
- Clutch 2 is in the transaxle.
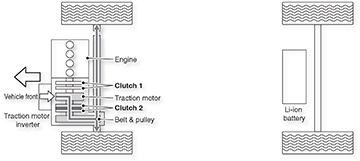
Rogue Hybrid
The Rogue Hybrid Intelligent Dual Clutch system uses two different clutches to split or combine the traction motor and gasoline engine to deliver power to the drive wheels.
The clutches are controlled by the TCM according to a command from Hybrid Powertrain Control Module [HPCM].
Clutch 1
Clutch 1 is included in the traction motor assembly. Clutch 1 is a dry clutch that consists of clutch drum, piston, drive plate, and driven plate.
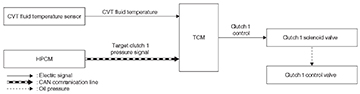
Clutch 1 Control System Diagram
TCM controls clutch 1 solenoid valve based on
- the CVT fluid temperature and
- the signal from the HPCM over the CAN line.
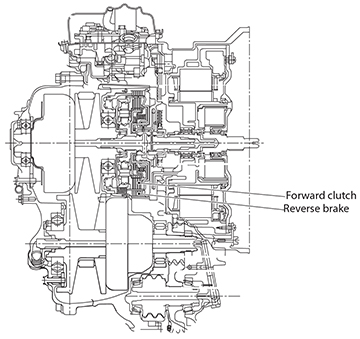
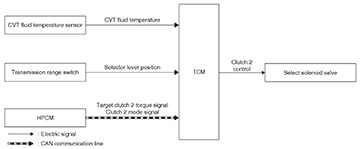
Clutch 2
Clutch 2 is actually made up of the forward clutch and reverse brake.
Clutch 2 control system diagram
TCM controls clutch 2 solenoid valve based on
- the CVT fluid temperature
- the transmission selector lever position, and
- the signal from the HPCM over the CAN line.
Examples of when the clutches are activated
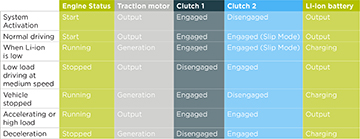
System Activation
During system activation, the gasoline engine starts, clutch 1 is engaged, clutch 2 is disengaged and the Li-ion battery sends power to the traction motor.
The starter motor can start the engine, but when the engine is cold or the Li-ion battery level is low, the traction motor output is used to start the engine by engaging clutch 1.
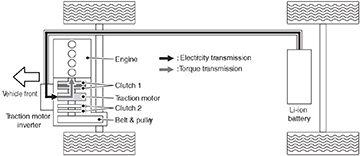
Normal Driving
During normal driving, the hybrid powertrain control module (HPCM) engages clutch 1 and starts engine, then engages clutch 2 (slip mode) and transmits engine output torque to drive wheels.
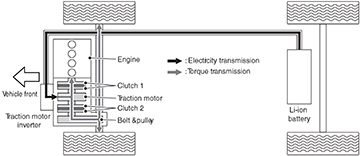
When remaining Li-ion battery level is low
When the Li-ion battery charge is low, the gasoline engine runs, clutch 1 is engaged, clutch 2 is engaged (slip mode) and the Li-ion battery is charging from the power sent to it from the traction motor.
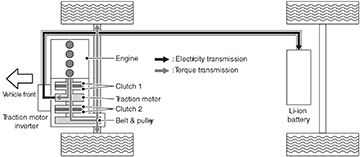
Low load driving at medium speed
When the vehicle is driving at medium speed with a low load, the gasoline engine is OFF, clutch 1 is disengaged, clutch 2 is engaged and the Li-ion battery sends power to the traction motor.
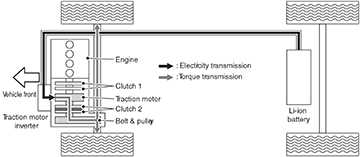
Vehicle Stopped
When the vehicle is stopped, the gasoline engine is running, clutch 1 is engaged, clutch 2 is disengaged and the Li-ion battery is charging from the power sent to it from the traction motor.
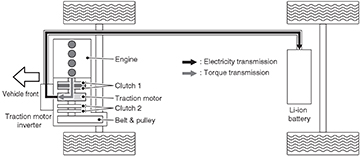
Accelerating or Load is High
When the vehicle is accelerating or the load is high, the gasoline engine is running, clutch 1 is engaged, clutch 2 is also engaged and the Li-ion battery sends power to the traction motor.
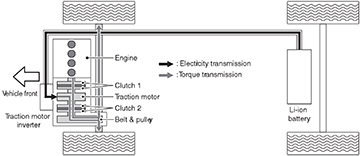
Deceleration Driving
When the vehicle is decelerating, the gasoline engine is stopped, clutch 1 is disengaged, clutch 2 is engaged and the Li-ion battery is charging from the power sent to it from the traction motor.
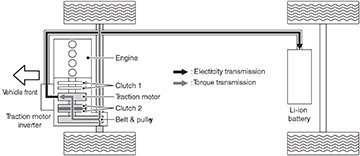
Clutch activation chart
Energy flow diagrams
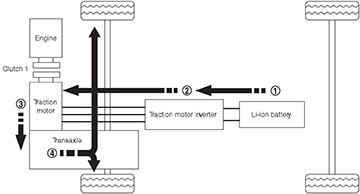
Flow from the Li-ion battery to the drive wheels
The energy flow to the drive wheels when the traction motor operates.
Energy flows from the:
- Li-ion battery to the
- Traction motor inverter to the
- Traction motor to the
- Transaxle and then to
- The drive wheels
Flow from the drive wheels to the Li-ion battery
The energy flow from the drive wheels to the Li-ion battery when the regenerative braking operates.
Energy flows from the:
- The drive wheels to the
- Transaxle to the
- Traction motor to the
- Traction motor inverter and then back into the
- Li-ion battery
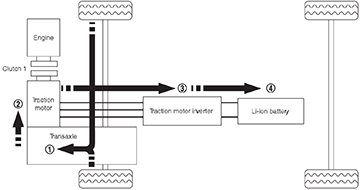
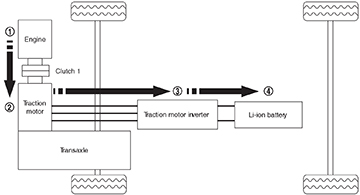
Flow from the engine to the Li-ion battery
The energy flow from the engine to the Li-ion battery.
Energy flows from the:
- The engine to the
- Traction motor to the
- Traction motor inverter and then to the
- Li-ion battery