TIRE LABELING
HOW TO READ THE TIRE LABEL
The numbers and letters on the sidewall give a lot of information about the tire.
Using a LT265/60 R 20 121/118R as our example, the following explains what these numbers and letters mean:
Reading Tire Size Codes
- Tire size specifications start with one of two letters that specify tire class:
- "LT" means light truck or SUV.
- In our example the LT tire is branded with two load indexes 121/118. The first number indicates the load carrying capacity for a singlewheel rear axle. The second number applies for a dual rear wheel application.

- A “P” in front of the numbers means that the tire is engineered to US passenger car standards.
- The three-digit number (in the art below,) indicates the tire's width in millimeters, measured from sidewall edge to sidewall edge.
- The tire's aspect ratio is the two-digit number listed after a slash to separate it from the tire class and width information. The aspect ratio is the height of the sidewall in relation to the tire's width.
- In our example, the number 60 means the sidewall's measured height is 60% of the tire's width.
- The width of the tire is 225 millimeters 225 x 0.60 = 135. The sidewall height is 135 millimeters.
- The letter after the aspect ratio indicates the internal construction type of the tire. The letter R on our example stands for Radial.
- Tire size codes end wth a two-digit number. This number refers to the diameter of the wheel or rim in inches, which the tire fits. In our example, the tire fits a "17 inch rim".
NOTE: Not all tires have a “P” specification; tires engineered to European metric standards do not have a letter before the tire size.

Tire Load and Speed Ratings
- The load index and speed rating for the tire are listed to the right of the tire size codes.
- The load index refers to the load-carrying capacity of a tire. This number is a measurement indicating the maximum weight each properly inflated tire can safely support. The larger the number, the higher load-carrying capacity the tires can handle.
- Tire speed ratings specifies a tires maximum sustainable speed. This letter signifies how fast the tire can be driven for a sustained period of time. V = 149 mph. The speeds are test speeds, not recommended speeds. The vehicle should never be driven faster than the tire speed rating.

TIRE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (TIN)
Federal law requires tire manufacturers to use a tire identification number or TIN. The TIN includes the:
- Manufacturer’s identification mark
- Tire size
- Tire type code (Optional additional code)
- The week and year the tire was built.
In our example, the Department of Transportation (DOT) code is on the left of the number, but it can be placed above, below or to the right of the number.
- The next two digits in our example are for the tire manufacturer’s identification mark.
- The next numbers indicate the tire size. The number after that is optional, so it won’t be found on all tires. If it’s on the tire, it is the tire type code.
- The last four digits indicate the week and year of tires manufactured after the year 2000. For example 2216 means the tire was built:
- 22nd week
- 2016 year

STANDARDS FOR TIRE WEAR
Tread wear, traction, and temperature resistance ratings are required on new pneumatic tires by the Uniform Tire Quality Grading (UTQG) system.
Part 575.104 of the Consumer Information Regulations requires that this information must be permanently molded into the tire sidewalls, indelibly stamped on a label or labels affixed to the tire tread surface, and made available in consumer brochures.
The UTQG apply to all passenger car tires except:
- deep tread, winter type snow tires,
- space-saver or temporary-use spare tires
- tires with nominal rim diameters of 12 inches or less, and
- limited production tires.

The treadwear grade is a comparative rating based on the wear rate of the tire when tested under controlled conditions expressed in two- or threedigit numbers.
The higher the number, the better the tread wear.
Tread wear grades are expressed in multiples of 20, like 80, 120, or 160.
The Traction Grade is based on a tire's straight line wet coefficient of traction as the tire skids under controlled conditions across controlled wet test surfaces.

The codes are:
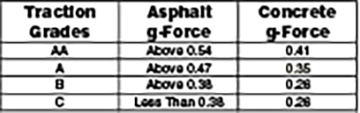
“AA” has the highest traction coefficient.
The UTQG Temperature Grade is the extent to which heat is generated and/or dissipated by a tire and its ability to dissipate heat when tested under controlled conditions. The temperature grades are A (the highest), B, and C.
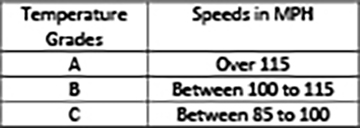
Sustained high temperature can cause the material of the tire to degenerate and reduce tire life, and excessive temperature can lead to sudden tire failure.
All passenger cars must meet at least grade C performance under the Federal Motor Safety Standard No. 109.
Grades B and A represent higher levels of performance on the laboratory test wheel than the minimum required by law.
![]()
The temperature grade for a tire is established for a tire that is properly inflated and not overloaded.
Excessive speed, under inflation, or excessive loading, either separately or in combination, can cause heat buildup and possible tire failure.

COMMON TIRE TYPES
Passenger tires
Passenger tires commonly include the following features and options:
- Higher profiles (80, 75, 70, or 65 series) for smoother ride and longer wear
- Lower speed ratings (Q, S, and T) with a harder, longer wearing compound
- All-season tread designs for year round wet, dry and snow traction
- Tread patterns that emphasize high ride comfort and low noise
- White or black sidewall finish
- Tread wear ranging from 30,000 to 85,000 miles or more

Touring tires
Touring tires commonly include the following features and options:
- Slightly lower profile (from 70 to 55 series) and wider tread than an equivalent passenger tire for improved handling and stability “at speed”
- The widest range of speed ratings (S, T, U, H and V) of any tire
- Numerous wear, handling, and ride quality performance in these areas varies depending on the tire
- Predominantly all-season tread designs (Although a number of dry or summer designs are available.)
- Tread patterns that emphasize performance blended with ride comfort and low noise
- Contemporary black sidewall styling (Few touring designs offer a white sidewall finish.)
- Optional tread wear guarantees, which diminish as speed ratings increase

Performance tires
Performance tires commonly include the following features and options:
- A very wide range of profiles and tread widths to select from for a special look (Muscle cars, vans and street trucks commonly use this tire type.)
- Typical speed ratings such as R, S and T are available
- All-season tread designs with year round wet, dry and snow traction
- Tread patterns that emphasize low speed traction and handling
- Raised white lettering or black lettering (on either sidewall) to provide styling choices
- Tread wear guarantees ranging from 40,000 to 50,000 miles

High Performance tires
High performance tires commonly include the following features and options:
- Lower profiles (as low as 40 series) and larger diameter wheel sizes (up to 17 inches) which stiffen sidewalls for improved cornering response, lower rolling resistance and increased tread stability
- H (130 mph) and V (up to 149 mph) speed ratings, help offer more control at higher speeds for high performance cars
- All-season designs (Although dry designs deliver superior cornering response and higher-speed stability in wet and dry conditions.)
- Tread designs with an emphasis on maximum contact patch
- Softer tread compounds for better traction
- Lower UTQG ratings and shorter tread life
- Sophisticated belt and cap ply packages that help maintain a maximum contact patch and optimum tire shape at high speeds
- Numerous bead and sidewall enhancements that stiffen the casing for better cornering response and higher-speed stability

Ultra High Performance tires
Ultra high performance tires commonly include the following features and options:
- The lowest profiles attainable by design and material technology, as low as 25 series, that deliver the greatest control and response at speed (Tire diameters up to 22 inches and cross-section widths up to 345 mm are available)
- Tested for high-top speed capabilities. Z (in excess of 149 mph), W (168 mph), and Y (186 mph)
- Asymmetric and directional tread designs that maximize dry contact patch and wet control (All-season designs are more tuned for performance or for year round usability)
- “Sticky” tread compounds that trade off tread life for performance (The UTQG tread wear ratings for ultra high performance tires are the lowest of any tire designed for everyday street use)
- Design innovations and lightweight materials to enhance handling and high-speed control

Winter Tires
Winter tires for cars and minivans are ideal for drivers who may encounter a wide range of potential winter conditions including snow, ice, slush, rain, and freezing rain. However, these tires remain applicable for dry highway conditions as well.
Winter tires commonly include the following features and options:
- Tread designs that balance a smooth, quiet ride (not much different than your “other” tires) with improved traction when bad winter weather develops
- Advanced design in tread compounds, including soft, microfilament grip materials that stay pliable in the coldest temperatures
- Superior snow and ice traction without the need for studs (Some designs allow for studding, however, for those who live in more extreme climates)
- Additional siping (very small slits in the blocks that give extra gripping edges across the treadface), which enhances traction for any road condition but is especially useful for snow and ice
- Q-, S- or T- speed rating for the everyday driver

Summer Tires
Summer tires provide superior performance on dry roads and include the following features:
- Summer tires are ideal for high performance vehicles, and are built for speed and agility. They offer increased responsiveness, cornering, and braking capabilities.
- The tread patterns of summer tires have less grooving and put more rubber in contact with the road. They are designed to provide maximum road-holding grip.
- The tread compounds of summer tires are designed to remain more flexible, allowing for better traction and grip. Summer tires may have shallower tread depths that allow for more stability when driven closer to their limits.

NOTE: Summer tires do not have the tire traction rating “M&S” on the tire sidewall.